Pvs vDisk Logon Process explained
Website Visitors:Citrix Provisioning Server (PVS) streams the contents of the vDisk to the Client VMs (target device) on demand, in real time. The Client VMs boot directly across the network and behaves as if it is running from its local drive. This article talks about various steps involved in network boot and how the vDisk is streamed.
Citrix Provisioning Services Network Boot Process
-
VM/Target Device is powered on
-
Device BIOS configured to perform a network boot
- (PXE/Network Boot)
-
- Used to extend the limitations of DHCP - By default, DHCP services are only able to allow target devices to send out a network broadcast limited to only the network/VLAN that it currently resides on. - Using an IP Helper allows the switching environment to identify that the DHCP Server(s) are physically located on a different network/VLAN. - Values of the IP Helper are simply the IP address of the associated DHCP Server(s).
-
Target device reaches and communicates with DHCP Server.
- DHCP network scope settings are configured for the specific network that the target device is physically located.
- DHCP Server allocates standard/basic network configuration values
- IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS Server(s)
- DHCP Server (in this special use case of PVS) also assigns some more advanced option setting and values.
- DHCP Option 66
- Used to provide the target device with a TFTP Boot Server
- TFTP boot server services are typically setup and configured on your actual PVS Servers.
- If needed, and on rare occasion, TFTP services can also be hosted on an isolated/dedicated infrastructure server.
- Used to provide the target device with a TFTP Boot Server
- DHCP Option 67
- Bootstrap file, boot file name
- Under a PVS environment, the default file name is ARDBP32.BIN
- Very common to use default file name, rarely changed from default name
- Under a PVS environment, the default file name is ARDBP32.BIN
- Bootstrap file, boot file name
- DHCP Option 66
-
Target Device Connectivity to Provided TFTP Server
- Target device connects to the TFTP server (typically a PVS Server) provided by DHCP services
- TFTP services reads associated bootstrap, boot file (ARDBP32.BIN) information to provide back to the client as a usable network boot server.
- TFTP bootstrap typically houses connectivity information for all of the PVS servers under your associated PVS Farm
- TFTP services reads associated bootstrap, boot file (ARDBP32.BIN) information to provide back to the client as a usable network boot server.
- Target device connects to the TFTP server (typically a PVS Server) provided by DHCP services
-
Target device communicates to the provided PVS Server and its associated running “Citrix PVS Stream Service”
- Target device MAC address lookup completed
- If there is an associated target device available under the PVS environment, it’s boot setting values are read and the target device is booted according to these settings.
- Target device MAC address lookup completed
High Level Boot steps
- First the target devices boots and acquires an IP address
- The target device first identifies a TFTP server
- Next the bootstrap file will be downloaded and the target device will be boot from it.
- The target device will contact and log onto one of the PVS servers.
- The logon server will notify the target device about the streaming server.
- Target device starts streaming the vDisk from the PVS server.
Just to summarize, PXE is used for getting the TFTP Server IP and bootstrap file name details by the clients and TFTP is used for downloading bootstrap program file.
Steps:
Let’s say, a Client VM is powered ON and it is configured to boot from Network.
Since it is configured to boot from network, it gets IP address from DHCP Server.
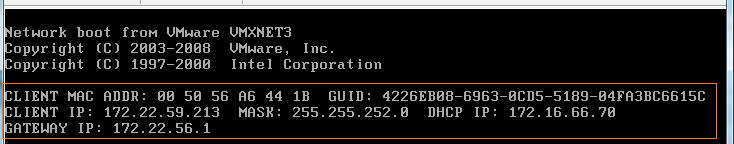
After getting IP Address from DHCP, Client sends broadcast request for PXE servers in the network. In general both PXE and TFTP services are provided by the PVS server itself.
Let’s say there are 2 PVS servers in the network having PXE service enabled. Both the PVS servers will respond to the client’s broadcast request
Client contacts the PXE server from which it receives the response first. PXE session is established
PXE service on PVS server sends the information of TFTP server IP address and name of the Bootstrap Program file to download from TFTP. The only use of PXE is to provide TFTP server details to clients.
Bootstrap program is a small program which initializes the streaming session between Client and PVS server.
Client establishes the TFTP connection to PVS Server and downloads the Bootstrap Program. The only purpose of TFTP service is to provide Bootstrap program to clients.

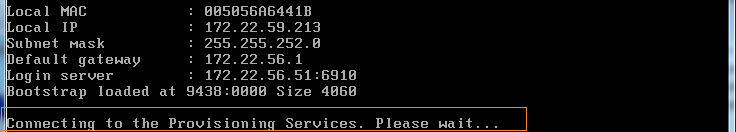
Bootstrap program file contains the information of which PVS servers to contact for vDisk download. In Citrix terminology, these servers are called Login servers (shown in above screenshot).
Bootstrap program contacts the PVS servers for vDisk. PVS checks its database for the target device mapped to client’s MAC address and the vDisk assigned to it.
Client establishes the streaming session to PVS Server. Client boots up with the OS image in the vDisk file
Just to summarize, PXE is used for getting the TFTP Server IP and bootstrap file name details by the clients and TFTP is used for downloading bootstrap program file.
Is there a way to eliminate PXE from the communication process?
Yes, by specifying TFTP Server IP Address and bootstrap file name in DHCP Scope options on DHCP Server. DHCP Scope options 66 and 67 can be used. DHCP server provides TFTP details to the clients along with dynamic IP address. Client VMs will directly contact TFTP server and download the bootstrap program.
Is there a way to eliminate both PXE and TFTP from communication process?
Yes, by using Boot Device Manager (BDM) both PXE and TFTP can be eliminated from communication process. Using Boot Device Manager utility on PVS Server, bootstrap file can be written into a ISO image, USB flash drive, or local hard drive. Client VMs need to be configured to boot from ISO image file. As ISO image file itself has bootstrap program, clients doesn’t use PXE or TFTP.
Posted in Experts-exchange
Understanding the Boot process in PVS
When a target device starts it needs to somehow be able to find and contact a provisioning server to eventually stream down the appropriate vDisk.This information is stored in a so-called Bootstrap file named ARDBP32.BIN. It contains everything that the target devcie needs to contact a pVS server so that streaming process can be initialized.
The boot strap file be delivered through a TFTP server, this also partly applies to the alternative BDM(Boot Device Manager)approach. There are some distinct differences between TFTP and BDM
TFTP
When using TFTP , target device needs to know how and where it can find the TFTP server to download the bootstrap file before connecting PVS server. TFTP can be configure in HA through Netscaler to avoid single point of failure. Provisoning services has its own built-in TFTP server. However, you are free to use whatever you prefer.
One of the most popular approach in delivering TFTP server address to your target devices is through DHCP, but there are other option as well..
BDM(Boot Device Manager)
There are actually two different methods to make use of the Boot Device Manager.
Let start with PVS, PVS offers a quick wizard which will generate a relatively small .ISO(around 300KB). Next , you configure your Target devices to boot from this .ISO file, using their CDROM/DVD players. This method uses a two-stage process where the PVS server location will be hardcoded into the bootstrap generated by BDM. The rest of the information like the (PVS device drivers) is downloaded from the PVS server using a TFTP protocol (UDP port 6969), here TFTP will still be used_._
As of XenDesktop version 7.x, when using XenDesktop setup wizard we can create and assign a small BDM hard disk partition, which will be attached to the virtual machine as a separate virtual disk. Using this method the above mentioned two-stage approach is no longer needed because partition already contains all the PVS drivers. This way all the information needed will be directly available without the need of PXE,TFTP & DHCP.
Note:
As and added advantage using the BDM method will also decrease the boot time by around 5 to 10 sec since we don’t have to wait for PXE and TFTP
Complete PVS Process is given HERE
Which of these is best to use?
DHCP Option: We cannot use only one PVS server while configuring DHCP scope option. We can enter multiple servers by comma-separated, but most of the clients goto the first server by default. So, for this, we have to use DNS round robin, or load balance TFTP with Netscaler AKA Citrix ADC.
PXE Method: You have to make sure that your target device, when booted can contact the PXE server ie., your target device and PXE server should be in same subnet. If you have more target devices, you have to configure from network level, so that your target devices can contact your PXE server. Normally, PVS server will have PXE and TFTP service.
BDM Method: Very simple and fast than other two options because, your target devices can directly contact PVS servers for bootstrap file. This option might be difficult if you have lot of physical machines.
More info on getting bootstrap file is given here: https://docs.citrix.com/en-us/provisioning/current-release/configure/configure-targets/bootstrap-file.html
Read this for more info:
https://www.techielass.com/dhcp-and-the-pxe-boot-process-explained
https://support.citrix.com/article/CTX227725
https://sjnbk.wordpress.com/2015/08/11/citrix-provisioning-services-7-6/#more-181
Want to learn more on Citrix Automations and solutions???
Subscribe to get our latest content by email.